GFB News Magazine
UGA teaching farmers to save water by scheduling irrigation
Posted on August 14, 2019 12:00 AM
UGA teaching farmers to save water by scheduling irrigation
Since 2017, 佐治亚大学农业用水效率小组(UGA AgWET)一直致力于帮助农民采用先进的灌溉调度工具,使他们能够根据作物用水需求来安排作物灌溉,从而节约用水. The team – made up of 16 UGA faculty with expertise in irrigation, water quality and quantity, 社会科学和青少年教育一直在共同努力执行这个项目.
该项目的农场部分侧重于对县推广人员进行智能灌溉战略培训,以便他们向农民传授知识.
Phone apps & soil sensors set schedules
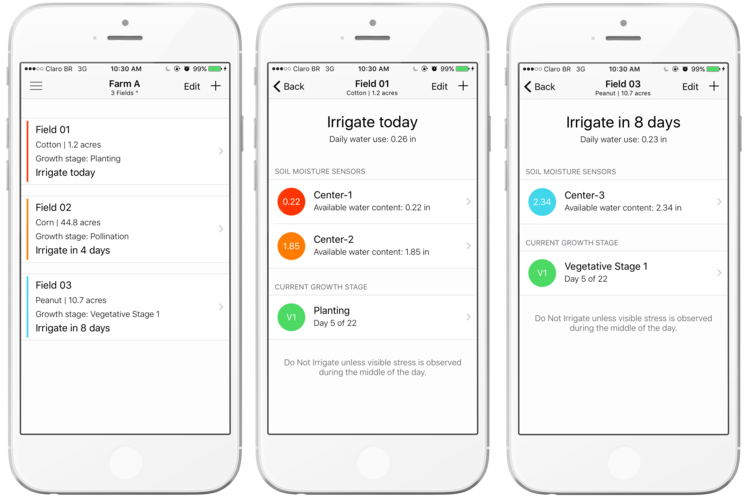
智能手机灌溉应用程序和土壤湿度传感器是该团队一直在培训农民使用中心支点灌溉系统的调度工具. 代理商正在与种植者合作,利用这些工具在他们的田地里安排灌溉,然后将结果与生产者的标准灌溉方法进行比较.
When the project started in 2017, the team had participating farmers in Burke, Bulloch, Coffee, Jenkins和Jeff Davis县(位于Extension的东南地区)和Colquitt, Decatur, Irwin, Miller, Sumter和Terrell县(位于Extension西南地区)使用这两种工具.
第一个是由UGA精密农业专家George Vellidis为Android和苹果智能手机开发的smartirirrigation棉花应用程序. The Cotton App (www.smartirrigationapps.Org)使用基于蒸散的模型来估计何时需要灌溉,并向用户提供应该施用多少水的估计. 它不需要任何传感器,在需要操作时向用户发送通知,而且是免费的. 缺点是需要精确的日降水数据才能达到最佳效果. 佐治亚州一个全州气象站附近的农民可以在应用程序中连接到气象站.
要求农民使用的第二种调度工具是格架土壤水分传感系统(www.trellis soil moisture sensing system).mytrellis.com). 它由三个探头和无线遥测组成,可以从任何能够上网的设备在线查看数据. The three probes, each with two soil moisture sensors placed at 6 and 14 inches deep, 安装在不同的土壤或地形区域,以证明内场变异性如何影响灌溉. 这有助于代理商和农民学习根据农田不同部分的保水情况做出有针对性的灌溉计划决策.
土壤水分发送系统的优点是直接测量田间土壤水分, 哪个比棉花应用程序所依赖的蒸散模型更能让农民有信心. Disadvantages of the soil moisture system are its initial expense, recurring costs, the need to install after planting and remove before harvest, 而且每个传感器只能测量探针周围狭窄半径内的土壤湿度.
Phase 2 of AgWET
In 2018, 县代理商继续与农民合作,使用棉花应用程序和网格土壤水分系统. The project added a social science component of surveys, focus groups and interviews to discover the agents’ and farmers’ beliefs, 与使用前后对调度工具的认知和采用相关的意见和行为变化.
Counties involved in the 2018 were: Appling, Burke, Bulloch, Jenkins, 杰夫戴维斯和威尔县(位于延伸的东南地区)和科尔奎特, Irwin, Macon, Mitchell, Sumter, Terrell and Turner counties (located in Extension’s Southwest District).
Expanding AgWET
This year, AgWET has entered Phase 3 of the project. In Southwest Georgia, UGA Extension is partnering with the Flint River Soil & 水资源保护区(FRSWCD)为未来两年在以下县开展的项目提供资金, Crisp, Decatur, Dooly, Miller, Mitchell, Sumter, Terrell and Thomas.
FRSWCD得到了东南水生资源伙伴关系(SARP)和国家鱼类的资助 & 野生动物基金会在未来三年内执行他们这边的项目. Counties that will be funded for the next three years include: Calhoun, Decatur, Dooly, Early, Grady, Miller, Mitchell, Randolph, Seminole and Terrell. Calhoun, Early, Grady, 兰多夫县和塞米诺尔县将使用灌溉计划应用程序灌溉花生,而不是棉花应用程序. 该项目的FRSWCD部分还包括位于阿巴拉契科拉-查塔胡奇-弗林特河流域的佛罗里达州北部和阿拉巴马州东南部的七个花生田.
Irrigator Pro is an irrigation scheduling tool for peanuts, corn and cotton developed by the USDA National Peanut Research Lab. 灌溉Pro的目的是提供基于科学数据的灌溉建议,旨在节约用水,同时保持高产.
The FRSWCD project in Calhoun, Early, Grady, 专注于花生灌溉的伦道夫县和塞米诺尔县将在每个农田只使用一个土壤湿度探测器,而不是三个. 每个探测器将配备三个传感器,位于8,16的深度 & 24 inches. The soil moisture probe is equipped with a soil thermometer and a rain gauge.
这款名为“灌溉者Pro”的应用程序通过云层从Trellis探测器上无线收集土壤湿度传感器数据和温度数据. The data is then sent to the app, 谁会根据土壤湿度读数和作物发育阶段提出灌溉建议.
This summer, county agents or crop consultants are also working with farmers in Dooly, Decatur, Miller, 米切尔和特雷尔县在棉花田使用棉花应用程序,在花生田使用灌溉专业应用程序.
Extension agents in Southeast Georgia continue to work with farmers in Appling, Bulloch, Burke, Irwin, Jeff Davis, Jenkins and Jefferson counties. Since there was no dedicated funding to look at specific crops, 代理商和农民可以自由选择作物和他们使用的调度工具. 所有代理商都选择使用土壤传感器,有些代理商决定将其与irrigation ator Pro一起使用. 一些代理商和农民正在使用调度工具来种植玉米和山核桃.
While soil moisture systems can cost farmers about $1,500 to buy (includes sensor station, base station and a 6-month data subscription), 灌溉专业版和smartirirrigation棉花应用程序可以通过苹果商店或谷歌Play商店免费下载和使用. 而smartirigation应用程序只能在苹果和安卓智能手机上使用, Irrigator Pro may be accessed via the Internet for use on personal computers.
Southwest District Extension Water Agent Cale Cloud and Dr. Wes Porter, UGA AgWET项目的成员,为本文提供了信息.