GFB新闻杂志
花生基因组定位加速了叶斑病研究
发布于2020年9月5日上午12:00
文/杰伊·斯通
For peanut growers, leaf spot isn’t the most front-of-mind challenge to growing a crop.
Tools to control leaf spot are readily available and are quite effective. The fungal disease and its prevention are simply part of the cost of doing business.
尽管如此,这个成本还是很大的.
“这是一个问题,乔治亚州花生委员会主任蒂姆·伯奇说, 他在贝克县的农场种植花生和棉花. “Last year it didn’t hit as hard, but the previous two years it was a big issue. 我用了全套(杀菌剂)程序. In ’18 I threw some more money at it late trying to stop it, but I had little success.”
The mingling of fungal diseases with peanut plants is inevitable without intervention, so much so that the UGA 2018 Peanut RX disease risk index refers to peanuts and fungal diseases as “an unavoidable union.”
农民们可能会说这是一个邪恶的联盟.
UGA Professor of Plant Pathology Bob Kemerait said there are five fungal diseases in the U.S. 这是每个种植花生的农民都应该知道的——早叶斑病, 晚叶斑病, 白霉病(也称为南方茎腐病), 根丝枯菌和枯菌.
其中,叶斑病构成了无处不在的威胁.
“美国的每一块花生田.S., even organic fields - and they would have lesser tools - every single one of them has to protect against leaf spot,克梅雷特说.
叶斑病使乔治亚州的花生种植者平均损失34美元.根据佐治亚大学的一项研究,从2005年到2009年,每年有600万. Left untreated, leaf spot can cut peanut crop yield by as much as 70%.
有没有办法减少或消除叶斑病的成本?
Dr. 科利·霍尔布鲁克正在努力寻找.
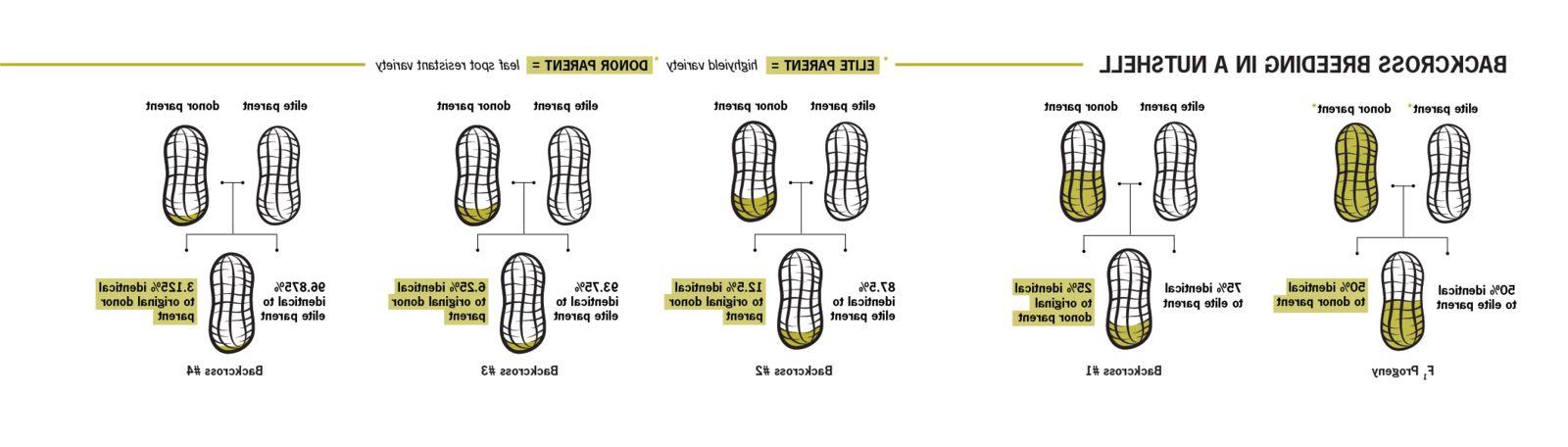
霍尔布鲁克, a peanut breeder with the USDA’s Agricultural Research Service (ARS) Tifton lab, 杂交花生35年了. 多样化的发展, 使用回交育种技术, can take 10 years or more before the desired combination of traits is achieved.
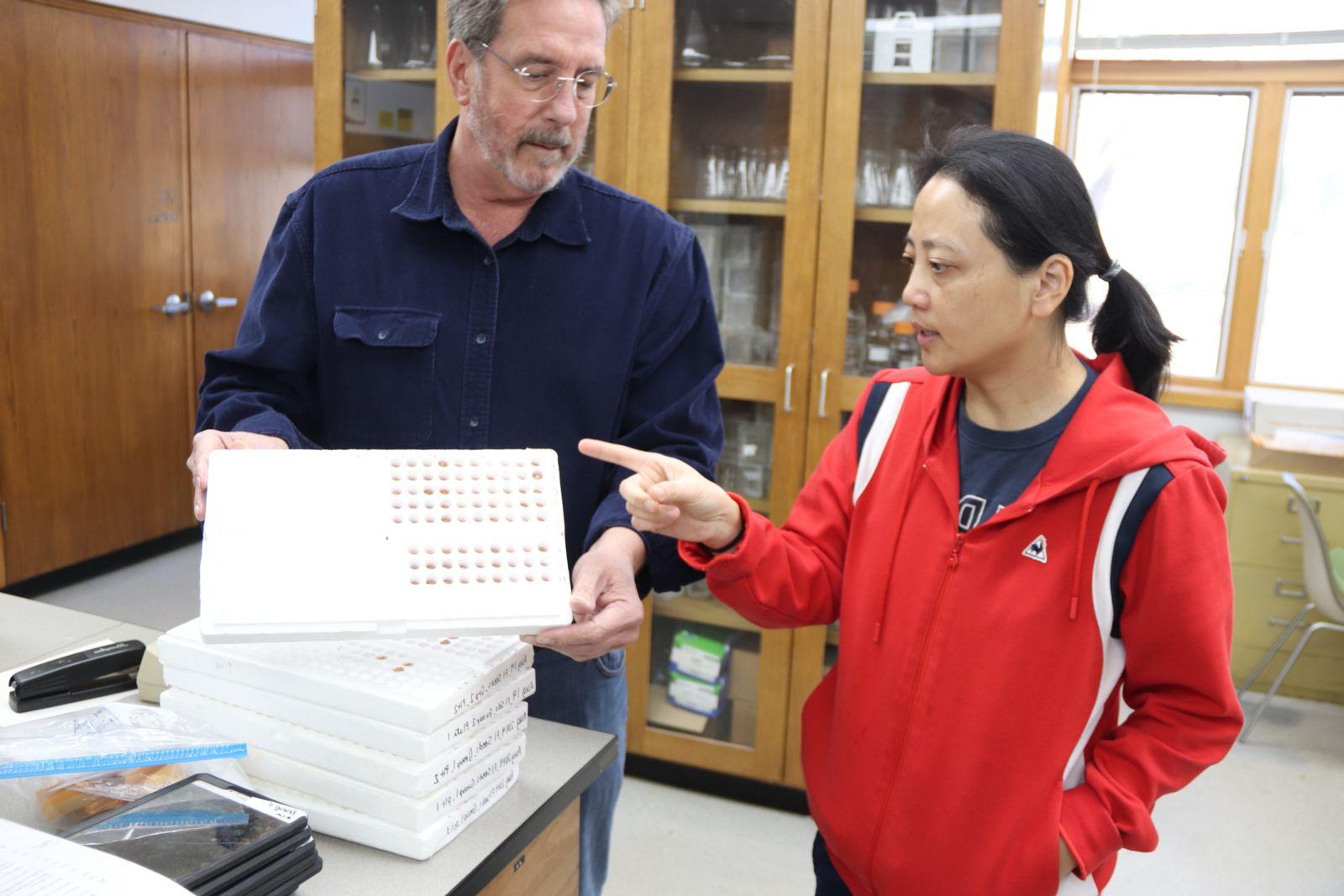

佐治亚大学研究员博士. 朱棣文(左)和美国农业部的朱棣文博士. Corley 霍尔布鲁克 discuss a breeding sample tray used in the process of marker-assisted selection. Each peanut in this tray is from a breeding line in the leaf spot study. A part of each peanut will be shaved off to extract and analyze DNA for presence or absence of certain traits.
杰伊·斯通摄
Backcross breeding entails taking a plant variety with a primary desirable trait and breeding it with another variety that has a different desirable trait.
在霍尔布鲁克的书房里, this involves crossing a high-yielding variety (TifNV-High O/L) with a breeding line variety resistant to a specific crop stressor, 比如引起叶斑病的真菌. 不幸的是,这种杂交不能产生可接受的产量.
A high-yielding peanut variety crossed with one that doesn’t yield well but is resistant to leaf spot results in a 50/50 distribution between the two varieties.
然后, 原来的高产品种被重新培育, 这次是第一次配对的结果, which expands the genetic contribution of the high-yield variety to 75%. 这是第一次回传.
Successive backcrosses increase the genetic contribution of the high-yielding variety by half each generation.
在叶斑的情况下, 霍尔布鲁克 said the first or second backcross could produce a leaf spot-resistant variety with outstanding yield and grade.
直到最近十年, the process was limited by the growth cycle of the plant; in peanuts this meant growing crossbred plants to maturity.
然后,新品种被重新种植,生长到成熟并进行测试. 然后整个循环又开始了下一代回交.
花生基因组图谱
In 2004, the American Peanut Council (APC) authorized the Peanut Foundation to set up a coordinated research effort to cut production costs while improving yield and quality. 同时, researchers were tasked with reducing the time it took to develop new peanut varieties, 在当时是12到15年.
This effort resulted in the establishment of the International Peanut Genome Initiative (IPGI).
花生正艰难地与其他作物竞争, 尤其是玉米, 棉花和大豆, 所有这些都是, 根据APC的估计, 品种发育比花生早6 ~ 10年. 到2010年,花生育种者已经鉴定出了大约6种,000 DNA molecular markers (fragments of DNA associated with specific traits). Not many were related to desired traits like drought tolerance or disease resistance. More than 100,000 useful DNA markers had been identified in corn and soybeans.
“我们知道这些工具需要应用于花生, 也, 让花生的改良跟上其他作物的步伐, so that it keeps peanut competitive and makes use of the newest breeding technologies,”医生说。. 佩吉Ozias-Akins, director of the National Environmentally Sound Production Agriculture Laboratory (NESPAL) on the campus of UGA-Tifton.
根据Ozias-Akins的说法, 与霍尔布鲁克共同担任IPGI执行委员会主席的人, there were scattered peanut genome-mapping studies being done before, but the research was extremely costly and no large-scale genome studies were underway.
IPGI has already developed a suite of DNA markers for nematode resistance, 以及各种TifNV-High O/L, 是霍尔布鲁克和奥齐亚斯-阿金斯合作开发的.
Collectively, these markers along with others could be used to combine, or stack, multiple traits. This process is referred to as breeding with marker-assisted selection, and it was one of three possible genetic research processes suggested for IPGI’s work. 另外两个, 基因改造(GMO)和突变育种, came with what the Peanut Foundation referred to as “significant drawbacks.”
The IPGI arranged a collaborative effort that included 135 researchers at 79 institutions in 20 countries. The APC and the Peanut Foundation provided $6 million over five years for the research.
使用基因组图谱
利用基因组的信息, 霍尔布鲁克 and his cooperators at the ARS and UGA labs in Tifton only have to grow enough plant material to extract DNA.
“In the past we would make a cross and then allow it to self-fertilize for a few years to produce progeny to test to see which one should be used in a backcross.霍尔布鲁克说. “You may be three or four years down the road before making a backcross. Now we can immediately begin the backcross because we have molecular markers.”
So now the process of a cross and three backcrosses only takes around five years, 为疾病控制提供更快的非化学解决方案.
For leaf spot-hating peanut farmers, faster solutions to their crop challenges are welcome news.
伯奇说:“这可能会使我们每英亩的成本降低50美元。. “这肯定会减少.”
Leaf spot was among the crop stressors the APC originally identified for targeted research, 但这并不是唯一的.
“你知道, there’s a lot of discoveries that are just waiting to be made in terms of disease resistance, 但花生的其他性状,比如质量,甚至更复杂的性状, 喜欢的味道, 我们对它了解不多, 至少在基因上, 此时此刻,奥兹亚斯-阿金斯说.